View and Download Ford SYNC owner's manual online. In-vehicle Bluetooth Communications System Powered by Microsoft. SYNC automobile accessories pdf manual download. An Azure file share in the same region that you want to deploy Azure File Sync. For more information, see: Region availability for Azure File Sync.; Create a file share for a step-by-step description of how to create a file share. Allway Sync – Synchronizer Service, Data Synchronization, Free File Synchronization, Backup, Data Replication, PC Sync Software, Freeware, File Sync, Data Synchronization Software. Download FreeFileSync for free. Free data backup software to synchronize files and folders. FreeFileSync is a free Open Source software that helps you synchronize files and synchronize folders for Windows, Linux and macOS. It is designed to save your time setting up and running data backups while having nice visual feedback along the way. Real Time Sync software synchronizes two or more folders and its files, that is, Real Time Sync makes sure that folders and all files in them are the same by copying the new or updated files from the folder where they appeared to the folder where they.
| 1. Introduction | |
| 5.1 Excluded Filter | |
| 8.1 General tab | |
1. Introduction
Real Time Sync software synchronizes two or more folders and its files, that is, Real Time Sync makes sure that folders and all files in them are the same by copying the new or updated files from the folder where they appeared to the folder where they are old or not present and by propagating deletions.
Real Time Sync can be used in these everyday scenarios:
- Synchronize notebook computer to desktop computer via local network.
- Keep user files in sync on work and home computer via USB key.
- Synchronize remote FTP and SFTP servers over the Internet.
- Incrementally Backup all files from main hard drive to portable hard drive or another computer.
In this Section we discuss challenges that synchronization programs face and that Real Time Sync successfully addresses.
1.1. Backup vs Synchronization
|
1.2. Why Synchronization Is Not Trivial
Synchronization task would appear to be trivial (compare file modification files and let the newer file win) if it was not for deletions that need to be propagated. If you delete file on one side, Real Time Sync will propagate this deletion to the other side of sync job by deleting this file on the other side. The sophistication of Real Time Sync algorithm allows us to propagate deletions correctly through multiple chained folders.
Another complication is that user may decide to replace newer version of the file with its older version. Real Time Sync can handle this situation correctly too, it will propagate the older file version, if it detects that user made such replacement.
1.3. Chained Synchronization
Chained syncing is a process when the contents of several folders (e.g., A, B, C and D) are synchronized by performing synchronization of pairs in sequence that results in propagation of changes (e.g., sync A and B, then B and C, then C and D results in changes in A propagating to folder B, then C, then D). Real Time Sync can perform Chained Syncing correctly.
You can use Real Time Sync chains to synchronize files between Computers that are not connected to each other. For instance, you can synchronize files between Work and Home computer using USB disk as an intermediary:
|
2. Using Real Time Sync
2.1 Synchronization Step By Step
Typical Real Time Sync user experience consists of these stages:
1. Select Folders To Synchronize User selects source and target folders to synchronize. | |
2. Comparative Analysis
| |
| |
|
2.2 Tasks
Each synchronized pair of folders is memorized in a Task. A Task also has a set of options that control various aspects of synchronization process. Each Task has a name that is requested when Task is created.
Real Time Sync memorizes list of Tasks and all their parameters per computer. Tasks can be created, deleted, renamed, analyzed and synced.
|
2.3 Synchronization Algorithm
This is a general outline of the synchronization algorithm (the actual algorithm is rather complex, it contains several important inventions and trade secrets that cannot be disclosed here):
|
2.4 Backup Files Incrementally: One Way Sync
For Real Time Sync, backup is a regular synchronization that happens one-way, as long as user does not manually change backup files which can cause conflicts. Only changed files and file deletions are propagated to backup folder. This is how you setup a backup:
|
2.5. Mini Window vs Main Window
Main Window contains the User Interface displayed to the user. It contains:
Home Tab: this is where you can create new tasks and start existing tasks.
|
Mini-Window or Mini-Mode is super-compressed summary of what is going on in Real Time Sync.
|
3. Actions
Action is a file/folder operation that is:
|
Each actions gets an icon in the center 3 columns of the tree.
See the next Chapter for the detailed list of actions icons.
3.1. Copy File Action
This is the most fundamental action of Real Time Sync. It copies files from Left to Right or from Right to Left. This action is represented by a green arrow in the direction of the copy.
3.2. Delete File Action
If Real Time Sync detects that a file has been deleted on the Left then selecting the delete Right action means that this file will be deleted from the Right. Likewise if Real Time Sync detects that a file has been deleted on the Right then selecting the delete Left action means that this file will be deleted from the Left. This way Real Time Sync propagates a deletion to the target folder. This action is represented by a green cross on the side of the file to be deleted.
3.3. No Copy Action
This action tells Real Time Sync not to do anything for this pair of files. Analyze sets this action to a pair if files are the same on both sides.
3.4. Conflict Action
If you changed the file on both sides of the synchronized folder pair then Real Time Sync cannot determine which version is preferred (because it does not know which set of changes should win and which should be dropped) and Real Time Sync then declares a conflict.
By default, conflict is a no-copy action. But you can change conflict into Left To Right or Rightt To Left Copy, thus declaring one side a winner.
3.5. Types of Conflicts
Real Time Sync may produce these types of conflicts:
|
3.6. Managing Time Shifts
FAT file system still used in Windows and some FTP servers have these problems:
|
Real Time Sync recognizes two types of Time Shifts:
|
3.7. Action Commands
All Action commands are available by right clicking on the item in the tree view.
Left to Right
Set action to Copy File Left to Right.
If the Left file exits then it will be copied to the Right.
If the Left file does not exist then the Right file will be deleted.
Right to Left
Set action to Copy File Right to Left.
If the Right file exits then it will be copied to the Left.
If the Right file does not exist then the Left file will be deleted.
Do Not Copy
Set action to No Copy.
As Recommended
Set action to what was recommended by Analyze.
4. Icon Descriptions
4.1. File Actions
File will be copied to the right side.
File will be copied to the left side.
File will be deleted from the right side.
File will be deleted from the left side.
4.2. Folder Actions
Files in the Folder will be copied to the right side.
File in the Folder will be copied to the left side.
Folder and all File will be deleted from the right side.
Folder and all File will be deleted from the left side.
Numbers next to the copy arrows indicate the number of files being copied in that direction.
4.3. Central Column
| Item is in sync. |
| User set this item action to No Copy. |
| Conflict. Real Time Sync can not decide how to sync this item, likely because item was modified on both sides. |
| Item has been synchronized. |
5. Filters
By default Real Time Sync synchronizes all files and folders that are not hidden and not system. Hidden and system files can be synchronized too, if the option to do so is turned on.
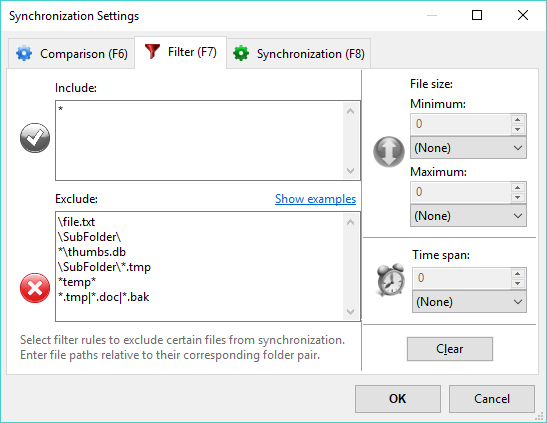
5.1. Excluded Filter
You may want to exclude some files and folders from synchronization by using Exclusions mechanism. For instance, object files *.OBJ and editor backup files *.BAK are usually excluded.To exclude the file or group of files add a filter to the Task:
|
To exclude read-only, hidden, or system files tick the appropriate box. To exclude a specific file name select the Add Name button and enter the name of the file you wish to exclude.
To exclude a specific file type (extension) select the Add Type button and enter the file extension you wish to exclude.
To exclude a specific folder name select the Add Name button and enter the name of the folder you wish to exclude.
By default Real Time Sync excludes hidden and system files and folders, because these files are not user files and usually they are not worth backing up or syncing. If you want Real Time Sync to see these files, uncheck 'Exclude hidden files' and 'Exclude system files' in Job -> Options -> Filters.
6. File Systems: Local and Remote
Not only can Real Time Sync synchronize disk and net shares mounted on your computer. It can also synchronize with Remote File Systems (FS) accessible through FTP and Secure FTP (SSH) protocols, Removable storage devices, and Windows Mobile devices.
To select or change your sync folder, start the Task wizard by selecting Add or Edit from the Home Tab.
Click Next until you reach the Source or Target Connection section.
Select the Add or Select button.
The Select Folder dialog appears.
File System Type appears in the left navigation pane of the Select dialog.
To change File System Type, click on different file systems on the left.
Then enter or edit your Remote Server Address in Address field (Remote FS only).
Then enter User Name, Password and maybe other connection data (Remote FS only).
Then click Connect button to connect to the server and test whether the data you entered is correct.
If connection is successful, the Home Folder of the User Name you used is shown and all folders below it.
Navigate to the folder to sync with in the folder tree.

If folder you want to sync with does not exist, create it:
Navigate to its parent folder and click New Folder button.
In this Section we provide detailed description of Local and Remote File Systems that Real Time Sync supports.
6.1. Local / Windows File System
Disks mounted directly on this computer.
Naming convention used: Windows 'disk letter + path', example: C:folder1folder2file.ext
Since no authentication is required and disks are always connected, the folder tree is shown right away (clicking Connect button is not needed).
Palm and Other USB Mass Storage Devices
These days Palm, Treo and many devices may present themselves as a regular Windows File System using USB Mass Storage Devices interface. Most Palm OS devices produced in the last 3-4 years can do that.
So if you have a Palm or Treo phone or PDA, you can sync its files with Windows desktop using Real Time Sync. Sync with Palm/Treo disk mounted to your Windows desktop, it will appear in Local tab.
Music and Media Players
You can also sync with Music and Media Players that show themselves as a Portable Disk using USB Mass Storage Devices interface. Such devices will also appear in Local tab.
For USB Mass Storage Devices and Media Players it is recommended that you use the Removable tab.
6.2. My Network / Windows Net Shares
Net Shares (remotely mounted disk volumes) available through Microsoft networking.
Naming convention used: Windows UNC, example: sharediskfolder1folder2file.ext
List of available network shares is shown, then you can drill down to the sync folder.
Enter the Username and Password if your share is password-protected by a User Name and Password that is different from the User Name and Password of the Windows account you are logged in to.
You can mount shares both from Local Network (LAN) and from remote computers (WAN).
Note that once you logged in to Share, Windows will cache authentication data. So if authentication data changes on server, you must Logout and then Login to you account on the client to make Windows use new authentication data.
6.3. Removable / USB Devices
Disks mounted on this computer.
Naming convention used: 'disk name + path', example: MyDiskfolder1folder2file.ext
Select the device you wish to connect to from the Drive drop down.
Since no authentication is required, the folder tree is shown right away.
As the drive letter for a removable device can change, for example it may be E: on one use and F: another time, Real Time Sync uses a unique hardware identifier to recognize removable devices. This means that Real Time Sync will always sync the specified device regardless of the drive letter assigned to it by Windows.
6.4. FTP
Remote FTP server.
Naming convention: URL without ftp:// or ftps:// prefix, example: server.domain.com/folder1/folder2/file.ext
User Name and Password are usually required.
If User Name and Password are empty, Real Time Sync uses User Name 'anonymous' and a blank Password.
6.5. Secure FTP (FTP over SSH)
Remote SSH server with SFTP capability.
Naming convention used: URL without sftp:// prefix, example: server.domain.com/folder1/folder2/file.ext
Works only with SSH-2 servers, not with SSH-1 servers.
Freehand mx 11. Authentication data is always required, and it comes in two different varieties:
|
6.6. Windows Mobile Phone and Pocket PC
Windows Mobile phones and Pocket PC devices.
Naming convention used: 'device name + path', example: MyPhonefolder1folder2file.ext
Device should be physically connected to the computer, usually it is plugged into USB port.
ActiveSync or Windows Mobile Device Center (WMDC) must be installed on the desktop.
Device is not required to have a partnership with desktop on which Real Time Sync is running.
So you can sync phone files with more than two desktops.
To sync with the phone that has no 'relationship' with your desktop: when ActiveSync tells you to create a new relationship upon connecting your phone to the desktop, select Guest Relationship or just press Cancel.
7. Task Options
Each Job has a set of options that modify the behavior of synchronization algorithm for this job.
7.1. Name / Type Tab
Sync Name
The name of the sync task, a descriptive name is recommended, this will help you recall the aim of the task when you next see the name.
Sync Method
Synchronization can be one of the eight ways, listed below.
One Way
Freefilesync Manual Pdf Free
|
Two Way
|
|
7.2 Source
Real Time Sync allows you to select common source paths, for example your Desktop of My Documents folder.
Alternatively you can select a number of specific folders using the Select Folder Manually function.
Select the Add button on the Source Connection panel, then browse to the desired folder.
Tick the folders you wish to sync with your target folder and select OK.
7.3. Filters Tab
Excluded (empty by default)
Files and folders that match any line on this list, will be excluded from synchronization.
Examples:
*.obj matched all files with .obj extension.
CVS matches all files and folder named CVS, anywhere in sync folders.
Exclude Read-Only Files and Folders
Exclude files and folders that have READONLY attribute.
Exclude Hidden Files and Folders
Exclude files and folders that have HIDDEN attribute.
Exclude System Files and Folders
Exclude files and folders that have SYSTEM attribute.
7.4. Schedule Tab
Freefilesync Manual Pdf
Real Time Sync can be made to run automatically by using this tab.
One or more events may be checked to cause automatic Sync:
On Windows start
Sync this task when Windows starts, Real Time Sync must be configured to start with Windows.
On Windows Shutdown
Analyze and then Sync this task just before Windows shutdown.
Note that Windows may try to kill Real Time Sync on shutdown. Normally Windows sees that Real Time Sync is performing file operations and responds to messages and it would let Real Time Sync finish. However this cannot be guaranteed.
On Disk Insert
Sync this task when a removable device is connected to your PC.
Real Time
Real Time Sync can detect when either the source or destination files change, this means that making a change to one file will automatically be replicated on the other side.
Note that this method is not recommended for FTP and SFTP connections as it will require considerable bandwidth.
Periodically (On Timer)
Sync this task periodically, every hours, minutes, days, or weeks.
You may specify a start date, that the schedule becomes active after.
Start time can be scheduled to specify when in the day to start the task.
Do Not Run
If you have schedules a task to run periodically you can specify specific days that the task should not be run on.
By default scheduled tasks can run on any day.
Auto Options work Only if Real Time Sync is Running
Real Time Sync must be already running for schedules events to work.
So you should turn on these global program options:
- Start Real Time Sync when Windows starts.
Job Scheduling
Each event that has just occurred flags the job as ready-to-run.
Ready-to-run jobs are run from left to right, sequentially, until all ready-to-run jobs have been run.
If job is already in the ready-to-run state and another even occurs that wants to run the job then this second event is ignored.
7.5. Advanced Tab
Save previous versions of deleted/replaced files (checked by default)
If checked then before overwriting a file in the source or target folder the original is moved to a backup folder to allow you to recover the original should you decide the change was not wanted.
Safe Copy using temporary files (checked by default)
If checked, then Sync does not copy source file directly to the destination file, as it would result in corruption of destination file is copy operation is aborted mid-way. Instead Sync copies source files to a temporary file in the destination folder and once copy operation is finished, temporary file is renamed to the destination file.
You may uncheck this option if you are doing 1-way backups and the destination volume has little free space, so that keeping two copies of one big file may overflow it.
Estimate disk space required (checked by default)
If checked Real Time Sync will estimate the amount of disk space needed to perform the synchronization process. This allows you to check that enough space is available before running the task.
Copy Locked Files (checked by default)
If On then copy from locked files using Volume Shadow service.
If Off then return Cannot Copy Locked File error.
Available on Vista and XP but not on Windows 2000.
Real Time Sync can copy only FROM locked file but never to LOCKED file.
Reconnect job folders
If checked Real Time Sync will attempt to reconnect to a remote server if the connection is lost, for example due to loss of internet connection.
Case-Sensitive File and Folder Names
If On then FILE.txt and file.txt will be treated as different file names.
Renames that change only file name case can be propagated even in Windows with this option On.
If not checked then FILE.txt and file.txt is treated as the same file name.
When changing this flag, you must Reset State for this task and re-sync all files.
Buffer Size
Specifies the buffer used when transferring files between two systems.
Conflict Action
This specified the default action to be taken if Real Time Sync detects a conflict between the source and destination files, for example if both files have been changed since the last sync.
|
8. Global Program Options
8.1 General tab
These global options apply to all jobs, to the entire Real Time Sync program.
Start Real Time Sync when Windows starts (off by default)
If checked then Windows starts Real Time Sync automatically when you log in to your Windows account.
Start minimized
Started this way, Real Time Sync shows only taskbar icon and no main window.
You can double-click the icon to call up the main Real Time Sync window.
Turn this option on if you run jobs automatically, that is, if you checked any boxed in Schedule tab.
Performance
Specify the maximum number of running tasks, this prevents lots of scheduled tasks from running at the same time and having a detrimental impact on your systems performance. If a task is scheduled and cannot be run as too many tasks are already running it will be queued and run when a task finishes.
Program priority can be set, this specifies how Real Time Sync should function when other programs are running, to make tasks run faster you can increase the priority, or to allow Real Time Sync to run in the background you can decrease the priority.
Log file size
If set then the log file will be restricted to a specific size. To unrestrict the size the log file can grow to enter zero.
Run missed scheduled tasks
If checked then scheduled tasks that were missed, for example because the computer was turned off, will be run when Real Time Sync is next launched.
Check for updates (on by default)
If checked then Real Time Sync will contact our servers daily to check whether the new version is available.
Reconnection
If during a sync the connection to the source or target is lost Real Time Sync can automatically attempt to reconnect. Enter the maximum number of reconnection attempt and the time between attempts before Real Time Sync cancels the task and reports the error.